转载 https://new.qq.com/rain/a/20201105A035BC00
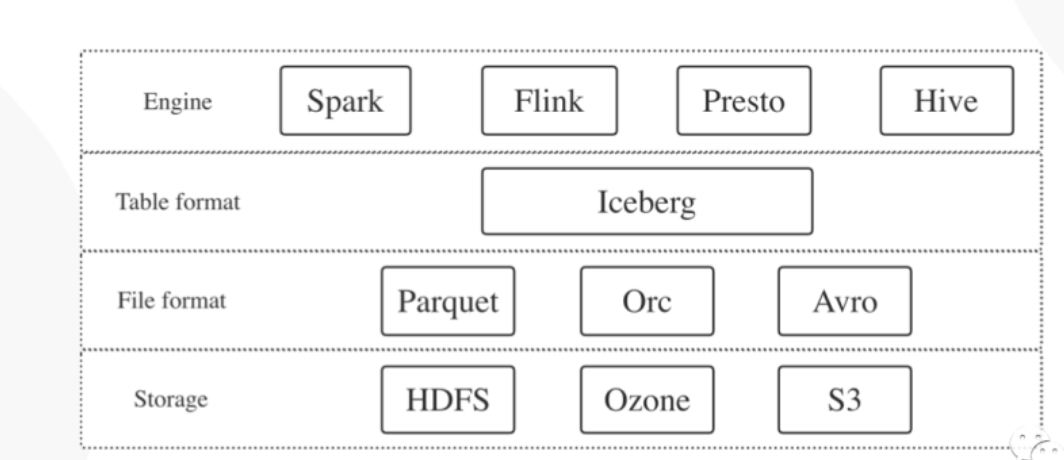
Iceberg
Apache Iceberg是一种新的表格格式,用于存储缓慢移动的表格数据。它旨在改进内置在Hive,Presto和Spark中的事实上的标准表布局。
设计的初衷更倾向于定义一个标准,开放且通用的数据组织格式,同时屏蔽底层数据存储格式的差异,向上提供统一的操作API,使得不同的引擎可以通过提供的API接入
Iceberg的核心思想
快照(snapshot)
在时间轴上线性的记录表的所有变化
1.在某一时刻,表的所有数据文件的列表
2.每次更新操作会生成新的快照,并且原子性的commit
3.实现 SnapshotManager
原子性
读写分离
时间旅行(数据版本)和版本回滚
增量消费
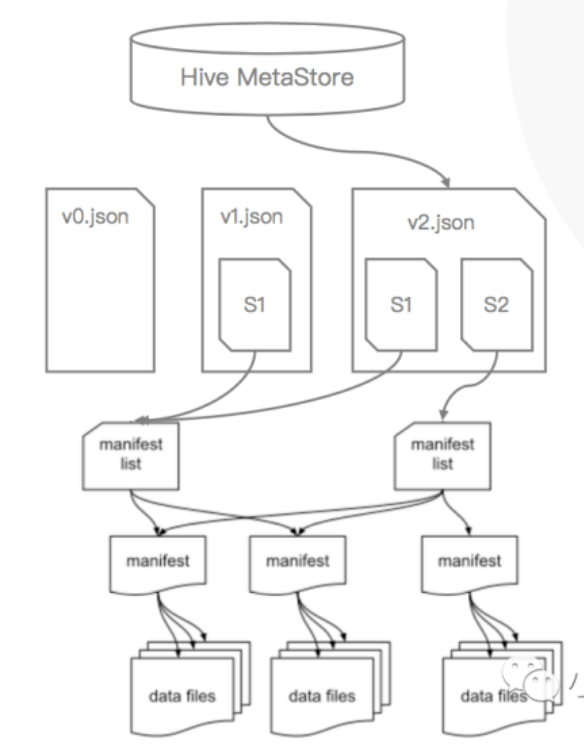
Iceberg的元数据管理
元数据
结构(schema)
分区信息
属性
快照历史记录
分层
HMS或文件内容
当前的元数据JSON文件
快照
Manifest list
Manifest
Data file
Iceberg的优势
优化数据入库流程
1.提供ACID事务能力(https://www.cnblogs.com/MopHunter/p/11232984.html),上游数据写入即可见,不影响当前数据处理任务,这大大简化了ETL
2.Iceberg 提供 upsert /merge into 能力,可以极大的缩小数据入库延迟 ()
统一数据存储和灵活的文件组织
1.批任务和流任务可以使用相同的存储模型(文件系统,对象存储),数据不再孤立
2.Iceberg支持隐藏分区和分区进化,方便业务进行数据分区策略更新
3.Parquet,ORC,Avro列存行存兼顾
支持更多的分析引擎
1.优秀的内核抽象使之不绑定于特定引擎,(Spark,Flink,Presto,Hive)
2.提供了对于流式的增量计算模型和基于批处理的全量表计算模型的支持
增量处理能力
1.Iceberg支持流式数据的落地和增量消费
2.Spark Structured Streaming适配
3.Flink sink/source 适配
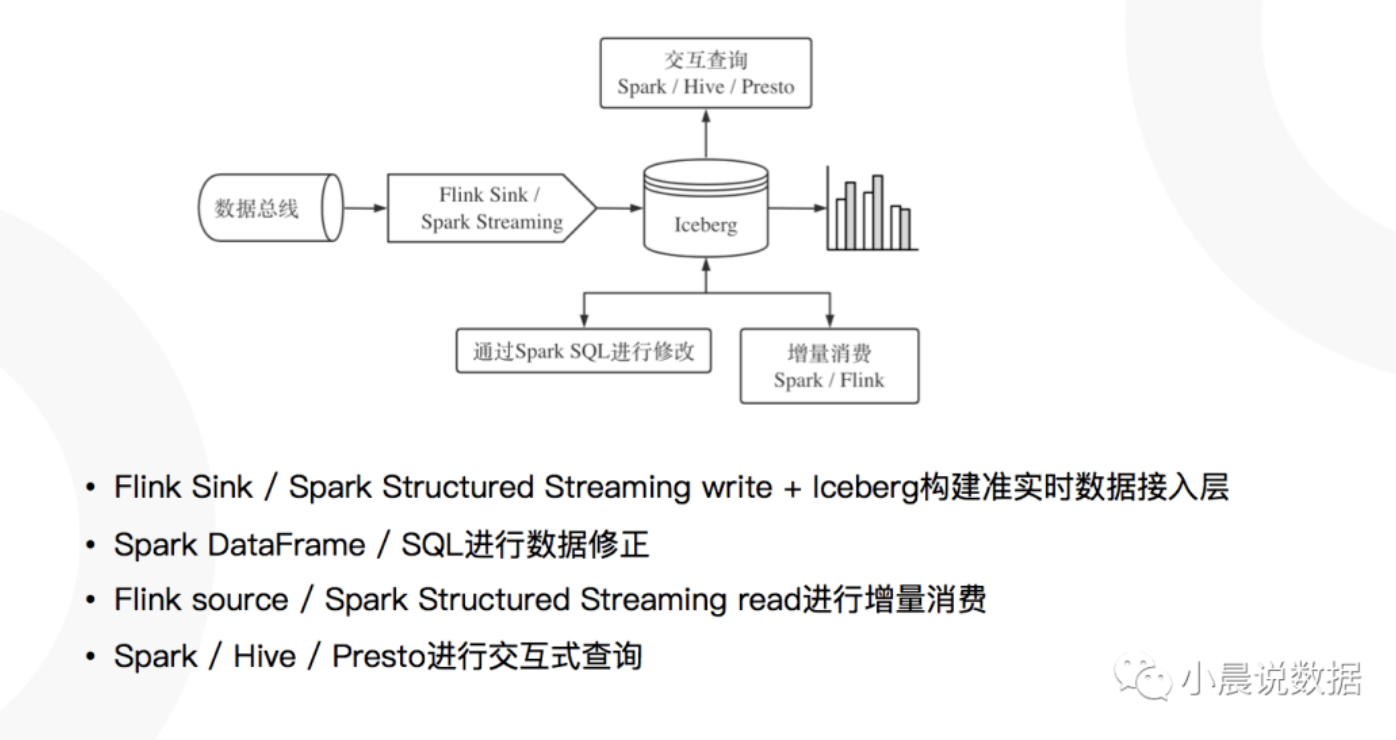
基于Iceberg的数仓构建
Flink Sink的基本原理
| 功能 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Writer | StreamOperator | 1.累积上游数据 ,在checkpoint发送barrier之前flush DataFile( preBarrierBeforeSnapshot) | |
| Committer | SinkFunction | 1.接收上游的DataFile信息, 在checkpoint时把DataFile信息填入ManiFest,并把Manifest写入state, 在checkpoint成功后向Iceberg commit | |
数据读写问题
数据读写没有ACID保证
数据没有版本控制
无法高效Update/Delete
分区管理不灵活
Iceberg 优势
1.更加开放的框架,既独立于上次计算又独立于下次存储
2.接口抽象程度高,兼容性好,迁移成本低
2.对各种引擎提供正对性的优化
Iceberg应用
HBase Source ->Flink ->Iceberg
对于修改记录采用Merge On Read的方式进行高效修改
Commit 生成Snapshot之后下游立刻可读
通过Iceberg 的时间旅行(Time Travel),访问历史版本数据成为可能
通过Iceberg的Snapshot机制,保证读取的ACID
大幅减少任务延迟时间,保证数据质量
用户行为流水按分钟粒度直接入库Iceberg
Commit生成Snapshot 之后下游立刻可读
结合Presto计算引擎构建 T+0准实时数仓
迟到数据可以轻松 Merge Into到 Iceberg表中
数据写入Iceberg的收益
1.减少入库依赖缓解,提高稳定性
2.数据实时性提高
3.数据实时性和数据价值正相关
4.迟到数据不再影响数据产出稳定性
Merge-On-Read Row-Level Delete
数据湖 Upsert技术优势
ACID & SNAPSHOT
1.读写分离,数据落地即可用
2.历史信息可追溯
Row-Level update
1.CDC增量更新
2.延迟数据修正
Table Evolution
1.文件组织方式更灵活,不再依赖目录分区
2.支持列增删改
Upsert 操作
这里要看一下 Flink DML操作
Merge INTO xxx.xxx using xxx
Upsert基本原理
Update+Delete+Insert操作集合,
这个操作以事务方式提交给表,
它的典型实现方式 :
CopyOnWrite
1.数据读出到内存,进行行更新后替换原理的文件
2.有点是后续读快,且不产生小文件
MergeOnRead
1.相关更新记录落地成Delta文件,读时进行合并
2.写速度快,会产生小文件问题
定义了两种Delta文件,基于位置的Position Delete和基于表达式的
Equality Delete,同时定义了Base File 和Delta File的序号来标识先后顺序以便进行合并操作
Upsert相关优化
upsert方式需要一些优化,例如添加索引支持,这样可以快速定位需要修改记录所在的分区和文件
Table操作的重要接口
/**
* Represents a table.
*/
public interface Table {
/**
* Return the full name for this table.
*
* @return this table's name
*/
default String name() {
return toString();
}
/**
* Refresh the current table metadata.
*/
void refresh();
/**
* Create a new {@link TableScan scan} for this table.
* <p>
* Once a table scan is created, it can be refined to project columns and filter data.
*
* @return a table scan for this table
*/
TableScan newScan();
/**
* Return the {@link Schema schema} for this table.
*
* @return this table's schema
*/
Schema schema();
/**
* Return the {@link PartitionSpec partition spec} for this table.
*
* @return this table's partition spec
*/
PartitionSpec spec();
/**
* Return a map of {@link PartitionSpec partition specs} for this table.
*
* @return this table's partition specs map
*/
Map<Integer, PartitionSpec> specs();
/**
* Return the {@link SortOrder sort order} for this table.
*
* @return this table's sort order
*/
SortOrder sortOrder();
/**
* Return a map of sort order IDs to {@link SortOrder sort orders} for this table.
*
* @return this table's sort orders map
*/
Map<Integer, SortOrder> sortOrders();
/**
* Return a map of string properties for this table.
*
* @return this table's properties map
*/
Map<String, String> properties();
/**
* Return the table's base location.
*
* @return this table's location
*/
String location();
/**
* Get the current {@link Snapshot snapshot} for this table, or null if there are no snapshots.
*
* @return the current table Snapshot.
*/
Snapshot currentSnapshot();
/**
* Get the {@link Snapshot snapshot} of this table with the given id, or null if there is no
* matching snapshot.
*
* @return the {@link Snapshot} with the given id.
*/
Snapshot snapshot(long snapshotId);
/**
* Get the {@link Snapshot snapshots} of this table.
*
* @return an Iterable of snapshots of this table.
*/
Iterable<Snapshot> snapshots();
/**
* Get the snapshot history of this table.
*
* @return a list of {@link HistoryEntry history entries}
*/
List<HistoryEntry> history();
/**
* Create a new {@link UpdateSchema} to alter the columns of this table and commit the change.
*
* @return a new {@link UpdateSchema}
*/
UpdateSchema updateSchema();
/**
* Create a new {@link UpdateProperties} to update table properties and commit the changes.
*
* @return a new {@link UpdateProperties}
*/
UpdateProperties updateProperties();
/**
* Create a new {@link UpdateLocation} to update table location and commit the changes.
*
* @return a new {@link UpdateLocation}
*/
UpdateLocation updateLocation();
/**
* Create a new {@link AppendFiles append API} to add files to this table and commit.
*
* @return a new {@link AppendFiles}
*/
AppendFiles newAppend();
/**
* Create a new {@link AppendFiles append API} to add files to this table and commit.
* <p>
* Using this method signals to the underlying implementation that the append should not perform
* extra work in order to commit quickly. Fast appends are not recommended for normal writes
* because the fast commit may cause split planning to slow down over time.
* <p>
* Implementations may not support fast appends, in which case this will return the same appender
* as {@link #newAppend()}.
*
* @return a new {@link AppendFiles}
*/
default AppendFiles newFastAppend() {
return newAppend();
}
/**
* Create a new {@link RewriteFiles rewrite API} to replace files in this table and commit.
*
* @return a new {@link RewriteFiles}
*/
RewriteFiles newRewrite();
/**
* Create a new {@link RewriteManifests rewrite manifests API} to replace manifests for this
* table and commit.
*
* @return a new {@link RewriteManifests}
*/
RewriteManifests rewriteManifests();
/**
* Create a new {@link OverwriteFiles overwrite API} to overwrite files by a filter expression.
*
* @return a new {@link OverwriteFiles}
*/
OverwriteFiles newOverwrite();
/**
* Create a new {@link RowDelta row-level delta API} to remove or replace rows in existing data files.
*
* @return a new {@link RowDelta}
*/
RowDelta newRowDelta();
/**
* Not recommended: Create a new {@link ReplacePartitions replace partitions API} to dynamically
* overwrite partitions in the table with new data.
* <p>
* This is provided to implement SQL compatible with Hive table operations but is not recommended.
* Instead, use the {@link OverwriteFiles overwrite API} to explicitly overwrite data.
*
* @return a new {@link ReplacePartitions}
*/
ReplacePartitions newReplacePartitions();
/**
* Create a new {@link DeleteFiles delete API} to replace files in this table and commit.
*
* @return a new {@link DeleteFiles}
*/
DeleteFiles newDelete();
/**
* Create a new {@link ExpireSnapshots expire API} to manage snapshots in this table and commit.
*
* @return a new {@link ExpireSnapshots}
*/
ExpireSnapshots expireSnapshots();
/**
* Create a new {@link Rollback rollback API} to roll back to a previous snapshot and commit.
*
* @return a new {@link Rollback}
* @deprecated Replaced by {@link #manageSnapshots()}
*/
@Deprecated
Rollback rollback();
/**
* Create a new {@link ManageSnapshots manage snapshots API} to manage snapshots in this table and commit.
* @return a new {@link ManageSnapshots}
*/
ManageSnapshots manageSnapshots();
/**
* Create a new {@link Transaction transaction API} to commit multiple table operations at once.
*
* @return a new {@link Transaction}
*/
Transaction newTransaction();
/**
* Returns a {@link FileIO} to read and write table data and metadata files.
*/
FileIO io();
/**
* Returns an {@link org.apache.iceberg.encryption.EncryptionManager} to encrypt and decrypt data files.
*/
EncryptionManager encryption();
/**
* Returns a {@link LocationProvider} to provide locations for new data files.
*/
LocationProvider locationProvider();
}
Spark 接入 Iceberg
Adding catalogs
(https://iceberg.apache.org/getting-started/#adding-catalogs)
Iceberg comes with catalogs that enable SQL commands to manage tables and load them by name. Catalogs are configured using properties under spark.sql.catalog.(catalog_name).
This command creates a path-based catalog named local for tables under $PWD/warehouse and adds support for Iceberg tables to Spark’s built-in catalog:
spark-sql --packages org.apache.iceberg:iceberg-spark3-runtime:0.9.1 \
--conf spark.sql.catalog.spark_catalog=org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkSessionCatalog \
--conf spark.sql.catalog.spark_catalog.type=hive \
--conf spark.sql.catalog.local=org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog \
--conf spark.sql.catalog.local.type=hadoop \
--conf spark.sql.catalog.local.warehouse=$PWD/warehouse
Creating a table
To create your first Iceberg table in Spark, use the spark-sql shell or spark.sql(...) to run a CREATE TABLE command:
-- local is the path-based catalog defined above
CREATE TABLE local.db.table (id bigint, data string) USING iceberg
Iceberg catalogs support the full range of SQL DDL commands, including:
Writing
(https://iceberg.apache.org/getting-started/#writing)
Once your table is created, insert data using INSERT INTO:
INSERT INTO local.db.table VALUES (1, 'a'), (2, 'b'), (3, 'c');
INSERT INTO local.db.table SELECT id, data FROM source WHERE length(data) = 1;
Iceberg supports writing DataFrames using the new v2 DataFrame write API:
spark.table("source").select("id", "data")
.writeTo("local.db.table").append()
The old write API is supported, but not recommended.
Reading
(https://iceberg.apache.org/getting-started/#reading)
To read with SQL, use the an Iceberg table name in a SELECT query:
SELECT count(1) as count, data
FROM local.db.table
GROUP BY data
SQL is also the recommended way to inspect tables. To view all of the snapshots in a table, use the snapshots metadata table:
SELECT * FROM local.db.table.snapshots
+-------------------------+----------------+-----------+-----------+----------------------------------------------------+-----+
| committed_at | snapshot_id | parent_id | operation | manifest_list | ... |
+-------------------------+----------------+-----------+-----------+----------------------------------------------------+-----+
| 2019-02-08 03:29:51.215 | 57897183625154 | null | append | s3://.../table/metadata/snap-57897183625154-1.avro | ... |
| | | | | | ... |
| | | | | | ... |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
+-------------------------+----------------+-----------+-----------+----------------------------------------------------+-----+
DataFrame reads are supported and can now reference tables by name using spark.table:
val df = spark.table("local.db.table")
df.count()
Flink Iceberg代码
Flink Source Sink Factory
@Override
public TableSource<RowData> createTableSource(TableSourceFactory.Context context) {
ObjectPath objectPath = context.getObjectIdentifier().toObjectPath();
TableLoader tableLoader = createTableLoader(objectPath);
TableSchema tableSchema = TableSchemaUtils.getPhysicalSchema(context.getTable().getSchema());
return new IcebergTableSource(tableLoader, tableSchema, context.getTable().getOptions());
}
@Override
public TableSink<RowData> createTableSink(TableSinkFactory.Context context) {
ObjectPath objectPath = context.getObjectIdentifier().toObjectPath();
TableLoader tableLoader = createTableLoader(objectPath);
TableSchema tableSchema = TableSchemaUtils.getPhysicalSchema(context.getTable().getSchema());
return new IcebergTableSink(context.isBounded(), tableLoader, tableSchema);
}
// 从 通过table路径 从 catalog
private TableLoader createTableLoader(ObjectPath objectPath) {
return TableLoader.fromCatalog(catalog.getCatalogLoader(), catalog.toIdentifier(objectPath));
}
//有 hadoop 和 hive的 catalog
class HadoopCatalogLoader implements CatalogLoader {
private final String catalogName;
private final SerializableConfiguration hadoopConf;
private final String warehouseLocation;
private HadoopCatalogLoader(String catalogName, Configuration conf, String warehouseLocation) {
this.catalogName = catalogName;
this.hadoopConf = new SerializableConfiguration(conf);
this.warehouseLocation = warehouseLocation;
}
@Override
public Catalog loadCatalog() {
return new HadoopCatalog(catalogName, hadoopConf.get(), warehouseLocation);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(this)
.add("catalogName", catalogName)
.add("warehouseLocation", warehouseLocation)
.toString();
}
//读进来的是个 DataFile
@Override
public void processElement(StreamRecord<DataFile> element) {
this.dataFilesOfCurrentCheckpoint.add(element.getValue());
}
// commit的时候
ManifestFile manifestFile =
SimpleVersionedSerialization.readVersionAndDeSerialize(FlinkManifestSerializer.INSTANCE, manifestData);
manifestFiles.add(manifestFile);
pendingDataFiles.addAll(FlinkManifestUtil.readDataFiles(manifestFile, table.io()));
if (replacePartitions) {
replacePartitions(pendingDataFiles, newFlinkJobId, checkpointId);
} else {
append(pendingDataFiles, newFlinkJobId, checkpointId);
}
//replace操作 就直接调用 ReplacePartitions 之类的
private void replacePartitions(List<DataFile> dataFiles, String newFlinkJobId, long checkpointId) {
ReplacePartitions dynamicOverwrite = table.newReplacePartitions();
int numFiles = 0;
for (DataFile file : dataFiles) {
numFiles += 1;
dynamicOverwrite.addFile(file);
}
commitOperation(dynamicOverwrite, numFiles, "dynamic partition overwrite", newFlinkJobId, checkpointId);
}
//如果是 append 就调用 Append方法
private void append(List<DataFile> dataFiles, String newFlinkJobId, long checkpointId) {
AppendFiles appendFiles = table.newAppend();
int numFiles = 0;
for (DataFile file : dataFiles) {
numFiles += 1;
appendFiles.appendFile(file);
}
commitOperation(appendFiles, numFiles, "append", newFlinkJobId, checkpointId);
}
Flink Catalog
public class FlinkCatalog extends AbstractCatalog {
private final CatalogLoader catalogLoader;
private final Catalog icebergCatalog;
private final String[] baseNamespace;
private final SupportsNamespaces asNamespaceCatalog;
private final Closeable closeable;
Flink Catalog 接口
// Create the default database if it does not exist.
open
close
listDataBases
databaseExists
createDatabase
listTable(String databaseName)
Iceberg部分
icebergCatalog = cacheEnabled ? CachingCatalog.wrap(originalCatalog) : originalCatalog;
这个 只是 个 CachingCatalog
@Override
public List<String> listTables(String databaseName) throws DatabaseNotExistException, CatalogException {
try {
return icebergCatalog.listTables(toNamespace(databaseName)).stream()
.map(TableIdentifier::name)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
} catch (NoSuchNamespaceException e) {
throw new DatabaseNotExistException(getName(), databaseName, e);
}
}
@Override
public CatalogTable getTable(ObjectPath tablePath) throws TableNotExistException, CatalogException {
Table table = loadIcebergTable(tablePath);
return toCatalogTable(table);
}
Table loadIcebergTable(ObjectPath tablePath) throws TableNotExistException {
try {
return icebergCatalog.loadTable(toIdentifier(tablePath));
} catch (org.apache.iceberg.exceptions.NoSuchTableException e) {
throw new TableNotExistException(getName(), tablePath, e);
}
}
@Override
public boolean tableExists(ObjectPath tablePath) throws CatalogException {
return icebergCatalog.tableExists(toIdentifier(tablePath));
}
@Override
public void dropTable(ObjectPath tablePath, boolean ignoreIfNotExists)
throws TableNotExistException, CatalogException {
try {
icebergCatalog.dropTable(toIdentifier(tablePath));
} catch (org.apache.iceberg.exceptions.NoSuchTableException e) {
throw new TableNotExistException(getName(), tablePath, e);
}
}
@Override
public void renameTable(ObjectPath tablePath, String newTableName, boolean ignoreIfNotExists)
throws TableNotExistException, TableAlreadyExistException, CatalogException {
try {
icebergCatalog.renameTable(
toIdentifier(tablePath),
toIdentifier(new ObjectPath(tablePath.getDatabaseName(), newTableName)));
} catch (org.apache.iceberg.exceptions.NoSuchTableException e) {
throw new TableNotExistException(getName(), tablePath, e);
} catch (AlreadyExistsException e) {
throw new TableAlreadyExistException(getName(), tablePath, e);
}
}
Iceberg 目录结构
Iceberg表支持在库模块中组织:
iceberg-common包含其他模块中使用的实用程序类iceberg-api包含公共的Iceberg APIiceberg-core包含Iceberg API的实现并支持Avro数据文件,这是处理引擎应依赖的东西iceberg-parquet是用于处理由Parquet文件支持的表的可选模块iceberg-arrow是用于将Parquet读入Arrow存储器的可选模块iceberg-orc是用于处理由ORC文件支持的表的可选模块iceberg-hive-metastore是由Hive Metastore Thrift客户端支持的Iceberg表的实现iceberg-data是用于直接从JVM应用程序中处理表的可选模块
Iceberg这个项目还具有用于向处理引擎添加Iceberg支持的模块:
iceberg-spark2是Iceberg 2.4版中Spark的Datasource V2 API的实现(使用iceberg-spark-runtime作为阴影版本)iceberg-spark3是Iceberg 3.0版Spark的Datasource V2 API的实现(阴影版本使用iceberg-spark3-runtime)iceberg-flink包含用于与Apache Flink集成的类(对阴影版本使用iceberg-flink-runtime)iceberg-mr包含一个InputFormat和其他用于与Apache Hive集成的类iceberg-pig是Pig的Iceberg的LoadFunc API的实现
文档信息
- 本文作者:Jessica
- 本文链接:https://jessica0530.github.io/2020/10/04/Iceberg/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)