SQL 基础算子讲解
Operator
Aggregate
MicroBatchGroupAggFunction
基本的聚合Operator,只能处理 key 没有明显的倾斜情况,并且key的重复率比较大来减少对 rocksdb的访问量,如果key没有重复 那性能和开不开 microbatch一致
//addInput
把处理的rowData存在List<RowData> buffer中
//finishBundle
到了触发批次的时间 调用 finishBundle
循环buffer的某个key,从 accState获取 该key上个批次累积的状态,
循环buffer中 key的数据,根据isAccumulateMsg对取出的状态做acc或者retract
如果generateUpdateBefore 需要 下发UPDATE_BEFORE,UPDATE_AFTER
如果不是 只需要下发INSERT
在 某个key的acc 的条数是 0的情况 说明 这条数据已经无效了,需要删除,需要往下发送 DELETE,并且清理该key的状态
MicroBatchIncrementalGroupAggFunction
优化 Partial-Final + Local-Global
IncrementalAggregateRule
**
* Stream physical RelNode for unbounded incremental group aggregate.
*
* <p>Considering the following sub-plan:
*
* StreamExecGlobalGroupAggregate (final-global-aggregate)
* +- StreamExecExchange
* +- StreamExecLocalGroupAggregate (final-local-aggregate)
* +- StreamExecGlobalGroupAggregate (partial-global-aggregate)
* +- StreamExecExchange
* +- StreamExecLocalGroupAggregate (partial-local-aggregate)
*
*
* partial-global-aggregate and final-local-aggregate can be combined as
* this node to share [[org.apache.flink.api.common.state.State]].
* now the sub-plan is
*
* StreamExecGlobalGroupAggregate (final-global-aggregate)
* +- StreamExecExchange
* +- StreamExecIncrementalGroupAggregate
* +- StreamExecExchange
* +- StreamExecLocalGroupAggregate (partial-local-aggregate)
*
*
* @see [[StreamExecGroupAggregateBase]] for more info.
*/
主要是 把partial-global-aggregate and final-local-aggregate 合并成一个IncrementalFunction,
在addInput里面 执行 partial-global-agg ,在finishBundle里面 做final-local-aggregate
--addInput
RowData currentAcc;
if (previousAcc == null) {
currentAcc = partialAgg.createAccumulators();
} else {
currentAcc = previousAcc;
}
partialAgg.setAccumulators(currentAcc);
partialAgg.merge(input);
return partialAgg.getAccumulators();
-- finishBundle
// pre-aggregate for final aggregate result
// buffer schema: [finalKey, [partialKey, partialAcc]]
Map<RowData, Map<RowData, RowData>> finalAggBuffer = new HashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry<RowData, RowData> entry : buffer.entrySet()) {
RowData partialKey = entry.getKey();
RowData finalKey = finalKeySelector.getKey(partialKey);
RowData partialAcc = entry.getValue();
// use compute to avoid additional put
Map<RowData, RowData> accMap = finalAggBuffer.computeIfAbsent(finalKey, r -> new HashMap<>());
accMap.put(partialKey, partialAcc);
}
for (Map.Entry<RowData, Map<RowData, RowData>> entry : finalAggBuffer.entrySet()) {
RowData finalKey = entry.getKey();
Map<RowData, RowData> accMap = entry.getValue();
// set accumulators to initial value
finalAgg.resetAccumulators();
for (Map.Entry<RowData, RowData> accEntry : accMap.entrySet()) {
RowData partialKey = accEntry.getKey();
RowData partialAcc = accEntry.getValue();
// set current key to make dataview know current key
ctx.setCurrentKey(partialKey);
finalAgg.merge(partialAcc);
}
RowData finalAcc = finalAgg.getAccumulators();
resultRow.replace(finalKey, finalAcc);
out.collect(resultRow);
}
Partial-Final
解决DISTINCT的热点问题,当Count(Distinct key) key的重复率不高的情况下,local 起不到预聚合作用的时候,需要手动的取Mod打散,比如
SELECT day, SUM(cnt) total
FROM (
SELECT day, MOD(buy_id, 1024), COUNT(DISTINCT buy_id) as cnt
FROM T GROUP BY day, MOD(buy_id, 1024))
GROUP BY day
SELECT SUM(b), COUNT(DISTINCT c), AVG(b) FROM MyTable GROUP BY a
flink logical plan:
FlinkLogicalCalc(select=[a, $f1, $f2, CAST(IF(=($f4, 0:BIGINT), null:INTEGER, /($f3, $f4))) AS
$f3])
+- FlinkLogicalAggregate(group=[{0}], agg#0=[SUM($2)], agg#1=[$SUM0($3)], agg#2=[$SUM0($4)],
agg#3=[$SUM0($5)])
+- FlinkLogicalAggregate(group=[{0, 3}], agg#0=[SUM($1) FILTER $4], agg#1=[COUNT(DISTINCT $2)
FILTER $5], agg#2=[$SUM0($1) FILTER $4], agg#3=[COUNT($1) FILTER $4])
+- FlinkLogicalCalc(select=[a, b, c, $f3, =($e, 1) AS $g_1, =($e, 0) AS $g_0])
+- FlinkLogicalExpand(projects=[{a=[$0], b=[$1], c=[$2], $f3=[$3], $e=[0]},
{a=[$0], b=[$1], c=[$2], $f3=[null], $e=[1]}])
+- FlinkLogicalCalc(select=[a, b, c, MOD(HASH_CODE(c), 1024) AS $f3])
+- FlinkLogicalTableSourceScan(table=[[MyTable,
source: [TestTableSource(a, b, c)]]], fields=[a, b, c])
'$e = 0' is equivalent to 'group by a, hash(c) % 256'
'$e = 1' is equivalent to 'group by a'
override def matches(call: RelOptRuleCall): Boolean = {
agg.partialFinalType == PartialFinalType.NONE && agg.containsDistinctCall() &&
splitDistinctAggEnabled && isAllAggSplittable
}
override def onMatch(call: RelOptRuleCall): Unit = {
// STEP 1: add hash fields if necessary
// STEP 2: construct partial aggregates
// STEP 2.1: expand input fields
// STEP 2.2: add filter columns for partial aggregates
// STEP 2.3: construct partial aggregates
// STEP 3: construct final aggregates
// STEP 4: convert final aggregation output to the original aggregation output.
// For example, aggregate function AVG is transformed to SUM0 and COUNT, so the output of
// the final aggregation is (sum, count). We should converted it to (sum / count)
// for the final output.
// Make a guarantee that the final aggregation returns NULL if underlying count is ZERO.
// We use SUM0 for underlying sum, which may run into ZERO / ZERO,
// and division by zero exception occurs.
// @see Glossary#SQL2011 SQL:2011 Part 2 Section 6.27
}
Expand 新增Expand关系表达式,其作用是对每条输入应用多组projects,然后得到多个输出,并将输出发送到下游。
可以在Grouping Sets里面用到
MicroBatchLocalGroupAggFunction + GlobalGroupAggFunction
主要解决 单个GroupBy节点数据热点问题,将原来的单GroupBy节点 分成Local+Global两个阶段来聚合
LocalGlobal本质上能够靠localAgg的聚合筛除部分倾斜数据,从而降低globalAgg的热点,提升性能
TwoStageOptimizedAggregateRule规则作用于 physicalPlan 产生之后。
负责将普通的DataStreamGroupAggregate 节点转成 DataStreamLocalGroupAggregate + DataStreamGlobalAggregate 两个节点。
Rule that matches [[StreamExecGroupAggregate]] on [[StreamExecExchange]]
with the following condition:
1. mini-batch is enabled in given TableConfig,
2. two-phase aggregation is enabled in given TableConfig,
3. all aggregate functions are mergeable,
4. the input of exchange does not satisfy the shuffle distribution,
and converts them to
StreamExecGlobalGroupAggregate
+- StreamExecExchange
+- StreamExecLocalGroupAggregate
+- input of exchange
override def matches(call: RelOptRuleCall): Boolean = {
//3个条件 开启microbatch和twoPhase,Agg需要实现merge,Input不能是hash不然热点都在local
isMiniBatchEnabled && isTwoPhaseEnabled &&
AggregateUtil.doAllSupportPartialMerge(aggInfoList.aggInfos) &&
!isInputSatisfyRequiredDistribution(realInput, agg.grouping)
}
//进行转换
override def onMatch(call: RelOptRuleCall): Unit = {
val globalHashAgg = createTwoStageAgg(realInput, localAggInfoList, globalAggInfoList, agg)
call.transformTo(globalHashAgg)
}
// the difference between localAggInfos and aggInfos is local agg use heap dataview,
// but global agg use state dataview
private def createTwoStageAgg(
input: RelNode,
localAggInfoList: AggregateInfoList,
globalAggInfoList: AggregateInfoList,
agg: StreamExecGroupAggregate): StreamExecGlobalGroupAggregate = {
val localAggRowType = AggregateUtil.inferLocalAggRowType(
localAggInfoList,
input.getRowType,
agg.grouping,
input.getCluster.getTypeFactory.asInstanceOf[FlinkTypeFactory])
// local agg shouldn't produce insert only messages
val localAggTraitSet = input.getTraitSet
.plus(ModifyKindSetTrait.INSERT_ONLY)
.plus(UpdateKindTrait.NONE)
val localHashAgg = new StreamExecLocalGroupAggregate(
agg.getCluster,
localAggTraitSet,
input,
localAggRowType,
agg.grouping,
agg.aggCalls,
localAggInfoList,
agg.partialFinalType)
// grouping keys is forwarded by local agg, use indices instead of groupings
val globalGrouping = agg.grouping.indices.toArray
val globalDistribution = createDistribution(globalGrouping)
// create exchange if needed
val newInput = satisfyDistribution(
FlinkConventions.STREAM_PHYSICAL, localHashAgg, globalDistribution)
val globalAggProvidedTraitSet = agg.getTraitSet
new StreamExecGlobalGroupAggregate(
agg.getCluster,
globalAggProvidedTraitSet,
newInput,
input.getRowType,
agg.getRowType,
globalGrouping,
localAggInfoList,
globalAggInfoList,
agg.partialFinalType)
}
Local+Global两个Function的具体实现
--Local
//addInput
在内存里面调用Acc accumulate和retract处理数据,把Acc结果存到Buffer中
// finishBundle
把 Buffer中的结果 发送给下游
-- global
//addInput
Input是个Acc, 做merge操作,结果存buffer中
//finishBundle
从state获取状态,把buffer中的结果merge进 状态里面,往下游发送数据更新状态
Join
PhysicalBiRel
1.joinInfo.isEqui 比如 join a.key = b.key
2.joinInfo.isEqui 比如 join a.key > b.key
val body = if (joinInfo.isEqui) {
// only equality condition
s"""
|${conversion.code}
|${generator.collectorTerm}.collect(${conversion.resultTerm});
|""".stripMargin
} else {
val nonEquiPredicates = joinInfo.getRemaining(this.cluster.getRexBuilder)
val condition = generator.generateExpression(nonEquiPredicates)
s"""
|${condition.code}
|if (${condition.resultTerm}) {
| ${conversion.code}
| ${generator.collectorTerm}.collect(${conversion.resultTerm});
|}
|""".stripMargin
}
val genFunction = generator.generateFunction(
ruleDescription,
classOf[FlatJoinFunction[Row, Row, Row]],
body,
returnType)
public interface FlatJoinFunction<IN1, IN2, OUT> extends Function, Serializable {
/**
* The join method, called once per joined pair of elements.
*
* @param first The element from first input.
* @param second The element from second input.
* @param out The collector used to return zero, one, or more elements.
*
* @throws Exception This method may throw exceptions. Throwing an exception will cause the operation
* to fail and may trigger recovery.
*/
void join (IN1 first, IN2 second, Collector<OUT> out) throws Exception;
}
lStateType, lMatchStateType, rStateType, rMatchStateType
6种 StateType
1.EMPTY, //do nothing
2.JOIN_KEY_CONTAIN_PRIMARY_KEY, //join keys contain pk.
//state格式<joinKey,record>
KeyedValueState<Row,Row> ,Tuple3<Row, Long, Long> reuse;
3.JOIN_KEY_NOT_CONTAIN_PRIMARY_KEY, //the record take primary key, but the pk isn't contain by the join keys.
//state 格式<joinKey, primaryKey, Tuple2<record,expire-time>>
KeyedMapState<Row, Row, Tuple2<Row, Long>> keyedMapState;
4.WITHOUT_PRIMARY_KEY, //the record don't take primary key.
//<joinKey, record, Tuple2<count, expire-time>>
KeyedMapState<Row, Row, Tuple2<Long, Long>> keyedMapState;
5和6 是 semi/anti join 不是join等值的情况下
5.COUNT_KEY_SIZE, //only keep the count size of join key.
6.COUNT_JOIN_KEY_CONTAIN_PRIMARY_KEY_SIZE (前提是Joinkey包含 primary key)// the count size of join key is no larger than one.、
MatchType 根据 Join的类型来判断
val (lStateMatchType, rStateMatchType) = joinType match {
case FlinkJoinRelType.INNER =>
(JoinMatchStateHandler.Type.EMPTY_MATCH, JoinMatchStateHandler.Type.EMPTY_MATCH)
case FlinkJoinRelType.LEFT =>
(inferMatchStateType(lStateType), JoinMatchStateHandler.Type.EMPTY_MATCH)
case FlinkJoinRelType.RIGHT =>
(JoinMatchStateHandler.Type.EMPTY_MATCH, inferMatchStateType(rStateType))
case FlinkJoinRelType.FULL =>
(inferMatchStateType(lStateType), inferMatchStateType(rStateType))
case FlinkJoinRelType.SEMI | FlinkJoinRelType.ANTI =>
(inferMatchStateType(lStateType), JoinMatchStateHandler.Type.EMPTY_MATCH)
}
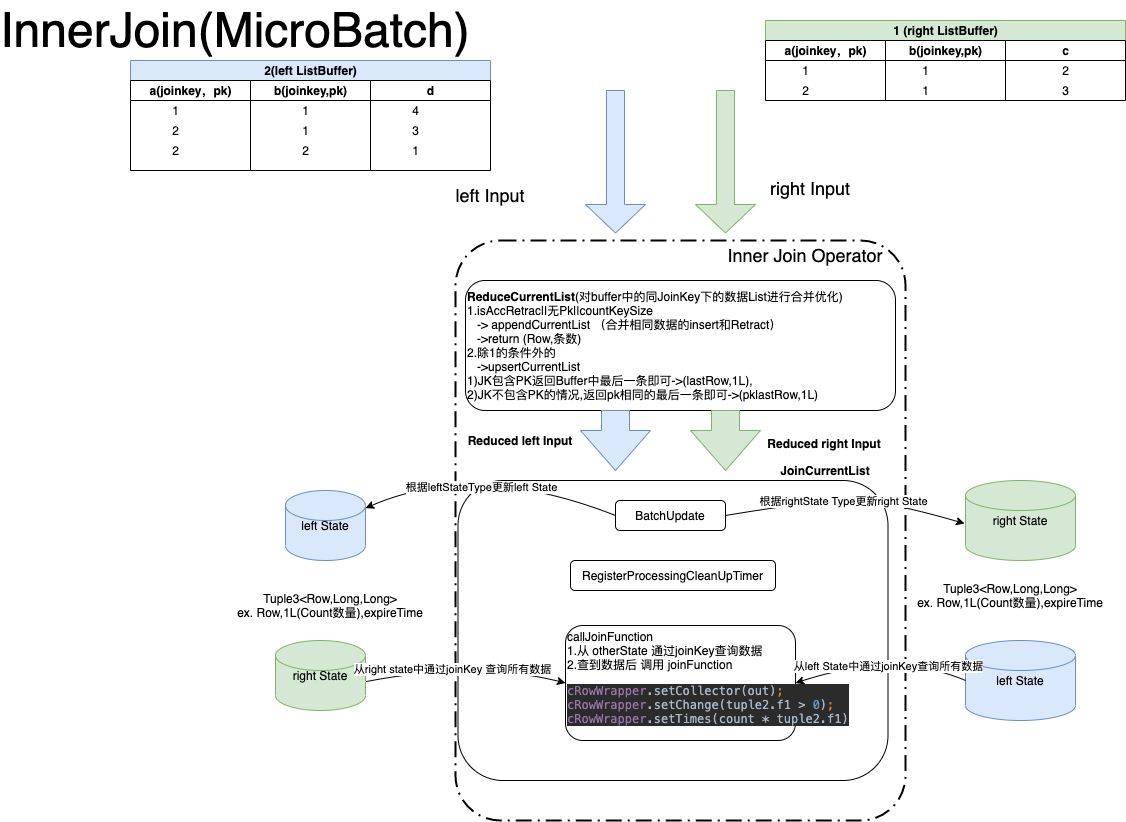
MicroBatchInnerJoinStreamOperator
InnerJoin l和rMatchType为 null所以只要传l和rStateType即可
InnerJoin本身不会产生回撤,如果他的上游 有个 回撤的消息,那更新自己State的时候会对回撤的key做remove操作
Retract消息会再和otherState做 join,往下游发送
MicroBatchOuterJoinStreamOperator
LefterOuterJoin 先处理 rightInput,RightOuterJoin先处理 leftInput,其他没啥区别
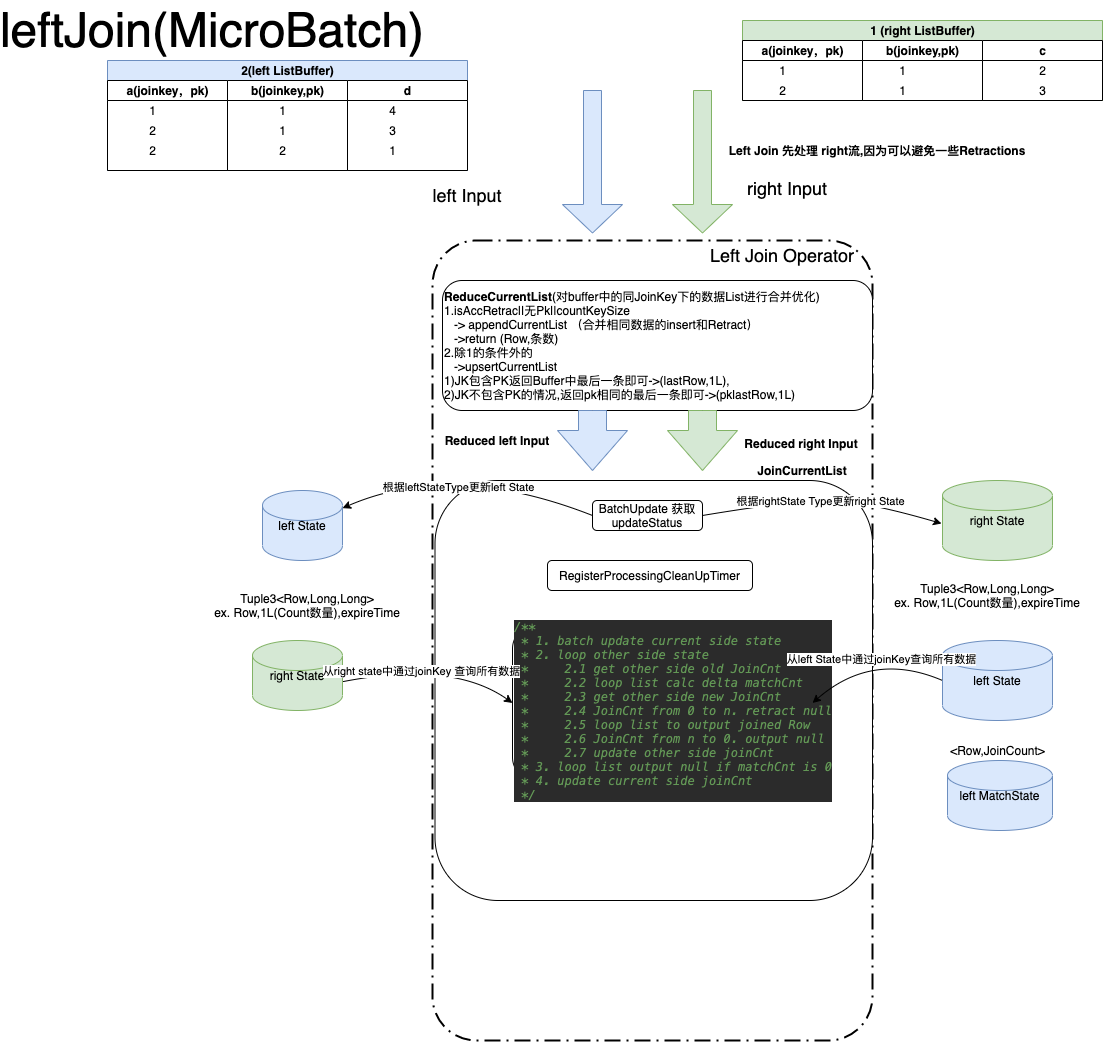
Outer Join 因为某些情况需要回撤,和修复数据, 所以 需要增加一个 MatchSize表示 该条数据 match上的条数。
以 left Join 举例
1.left Join 先来一条数据 + (1,1)joinKey,3, 但这个时候 右流的State没有数据,那需要补空发送 +(1,1),3,null 下去,并且leftMatch[(1,1),0]表示 该joinkey join到的条数为0
2.如果 right 来了条 +(1,1),4,发现 之前left那条数据现在是可以 join上的, 那leftMatch 0 ->1, 这个时候需要 回撤 null的数据,更新最新的数据 [ -(1,1),3,null] [+(1,1),3,4]
3.如果 right 来了条回撤的数据 -(1,1),4 ,说明需要回撤掉上一条数据,那 left的match需要 回归为0,leftMatch 1->0
需要 [-(1,1),3,4] ,[+(1,1),3,null]
一般什么情况下会有 回撤数据, 说明这条数据是无效的,比较常见的情况是 上游输入是个groupby算子,把group by的聚合算子的结果作为了一个 pk,
但是聚合的结果是会变的,如果从 3->4,那 pk为3的这条数据就 无效了,那必须要删除
MicroBatch SEMI-ANTI Joiner
SEMI 为例 where a in/Exists (SubQuery)
SubQuery -> SemiJoin->FlinkLogicalSemiJoin ->DataStreamJoin(joinType-Semi)
优化规则
1.FlinkSemiJoinJonTransposeRule
SELECT * FROM x, y WHERE x.c = y.f AND EXISTS (SELECT * FROM z)
SemiJoin(LogicalJoin(X, Y), Z) ->LogicalJoin(SemiJoin(X, Z), Y)
2.FlinkSemiJoinProjectTransposeRule
SemiJoin(LogicalProject(X), Y) -> LogicalProject(SemiJoin(X, Y))
TimeWindow Join

over
rank
Rank 具体算子包括:Row_NUMBER,RANK,DENSE_RANK
row_number的用途非常广泛,排序最好用它,它会为查询出来的每一行记录生成一个序号,依次排序且不会重复,注意使用row_number函数时必须要用over子句选择对某一列进行排序才能生成序号。比如 1 2 3 相同的值也1 2 3
rank函数用于返回结果集的分区内每行的排名,行的排名是相关行之前的排名数加一。简单来说rank函数就是对查询出来的记录进行排名,与row_number函数不同的是,rank函数考虑到了over子句中排序字段值相同的情况,如果使用rank函数来生成序号,over子句中排序字段值相同的序号是一样的,后面字段值不相同的序号将跳过相同的排名号排下一个,也就是相关行之前的排名数加一,可以理解为根据当前的记录数生成序号,后面的记录依此类推。 比如相同的值 1 1 3
dense_rank函数的功能与rank函数类似,dense_rank函数在生成序号时是连续的,而rank函数生成的序号有可能不连续。dense_rank函数出现相同排名时,将不跳过相同排名号,rank值紧接上一次的rank值。在各个分组内,rank()是跳跃排序,有两个第一名时接下来就是第三名,dense_rank()是连续排序,有两个第一名时仍然跟着第二名。相同的值是 1 1 2
-每门课程第一名只取一个:
select * from (select name,course,row_number() over(partition by course order by score desc) rank from student) where rank=1;
--每门课程第一名取所有:
select * from (select name,course,dense_rank() over(partition by course order by score desc) rank from student) where rank=1;
--每门课程第一名取所有:
select * from (select name,course,rank() over(partition by course order by score desc) rank from student) where rank=1;
算子需要实现的接口
//处理 insert type的record with rank number
processInsertWithNumber(Row sortKey,Row input,long rankEnd,TopNBuffer buffer)
//处理 insert type的record without rank number
processInsertWithoutNumber(Row sortKey,Row input,TopNBuffer buffer,long rankStart,long rankEnd)
//处理 retract type的record with rank number
processRetractWithNumber(Row sortKey,Row input,long rankEnd,TopNBuffer buffer)
//处理 retract type的record without rank number
processRetractWithoutNumber(Row sortKey,Row input,TopNBuffer buffer,long rankStart,long rankEnd)
//处理 update type的record with rank number
processUpdateWithNumber(Row sortKey,Row input,long rankEnd,TopNBuffer buffer)
//处理 update type的record without rank number
processUpdateWithoutNumber(Row sortKey,Row input,TopNBuffer buffer,long rankStart,long rankEnd)
//get rank number and inner rank number
Tuple2<Integer, Integer> rowNumber(Row sortKey, Row inputRow, TopNBuffer<Row> buffer);
Rank Opeator 有3种 AppendFastRank,UpdateFastRank,RetractSortedRank
def analyzeRankStrategy(
rankType: RankType,
input: RelNode,
partitionKey: ImmutableBitSet,
orderKey: RelCollation,
mq: RelMetadataQuery): RankStrategy = {
//字段排序规则
val fieldCollations = orderKey.getFieldCollations
//input 是否是个Update流
val isUpdateStream = !UpdatingPlanChecker.isAppendOnly(input)
if (isUpdateStream) {
val fmq = FlinkRelMetadataQuery.reuseOrCreate(mq)
//获取上游的pk,如果是 group by 的话pk是 groupby字段
val uniqueKeys = fmq.getUniqueKeys(input)
//如果 如果上游 uniquekey不包含partitionKey的话,会产生无效的数据,必须要用能回撤的Rank
if (uniqueKeys == null || uniqueKeys.isEmpty
// unique key should contains partition key
|| !uniqueKeys.exists(k => k.contains(partitionKey))) {
// input is AccRetract or extract the unique keys failed,
// and we fall back to using retract rank
RetractSortedRank
} else {
//如果不是 update流
val fmq = FlinkRelMetadataQuery.reuseOrCreate(mq)
val monotonicity = fmq.getRelModifiedMonotonicity(input)
//看上游数据的单调性
val isMonotonic = if (monotonicity == null) {
false
} else {
if (fieldCollations.isEmpty) {
false
} else {
fieldCollations.forall { collation =>
val fieldMonotonicity = monotonicity.fieldMonotonicities(collation.getFieldIndex)
val direction = collation.direction
if ((fieldMonotonicity == SqlMonotonicity.DECREASING
|| fieldMonotonicity == SqlMonotonicity.STRICTLY_DECREASING)
&& direction == Direction.ASCENDING) {
// sort field is ascending and its monotonicity is decreasing
true
} else if ((fieldMonotonicity == SqlMonotonicity.INCREASING
|| fieldMonotonicity == SqlMonotonicity.STRICTLY_INCREASING)
&& direction == Direction.DESCENDING) {
// sort field is descending and its monotonicity is increasing
true
} else if (fieldMonotonicity == SqlMonotonicity.CONSTANT) {
// sort key is a grouping key of upstream agg, it is monotonic
true
} else {
false
}
}
}
}
if (isMonotonic && rankType.equals(RankType.ROW_NUMBER)) {
//如果有单调性 用 UpdateFastRank
UpdateFastRank(uniqueKeys.iterator().next().toArray)
} else {
RetractSortedRank
}
}
} else {
AppendFastRank
}
}
AppendFastRank
场景: 上游的input stream 是 Append-Only,比如上游是个 kafka source,那只需要根据字段里面的sortKey来进行排序
1.checkSortKeyInBufferRange TopNBuffer 是个 treeMap<sortKey,Collection<Data>>
先check 当前数据的sortKey 是否在Rank范围内
2. 不在的话 不进行处理
3. 在的话 buffer中先put该sortkey和数据,在dataState中也更新该数据,
4. processElementWithRowNumber的情况下,把受影响的数据进行更新 ,发送 before和after数据,并且把已经从 topN删除的数据 从 state和 buffer中删除
5. processElementWithoutRowNumber 的情况下
buffer 获取当前TopNum 如果大于rankEnd的话
删除 lastKey 并且collectDelete ,再collectInsert 当前值,并且更新 buffer.remove和 datastate.remove
UpdateFastRank
场景:上游是个 update stream,比如 group by ,left join,emit窗口,是 RetractSortedRank的优化版本
比如以下场景
聚合大类下的店铺的订单金额,再根据这个金额找到大类下 销售最高的前10个店铺
这种情况 上游的unique_key包含 partition key,且聚合函数是单调递增 且排序是降序的情况下,因为可以 只保存 前TopN的数据,就可以用 UpdateFastRank优化
为啥 单调递增 且排序也是升序的不能优化,因为 降序可以保证 新加入排名的数据 只是在 TopN中的数据 踢掉最后一名的数据, 但是 降序的话,因为 他是递增的 所以会导致自己的数据 会被排除再topN外,那就需要给TopN补数,那就不能只保存前TopN的数据
SQL例子
Select sum(order) as order_sum, catagoryId,shopId from table group by catagoryId,shopid
Select shopid,row_number over (partition by catagoryid order by order_sum desc) as rank where rank <=10
1.order by字段是升序的并且上游数据聚合函数是单调递减的,或者orderby 字段是降序的并且聚合函数是上游单调递增,比如sum 是 递增的
Input data 有唯一的主键 比如 group by keys
Input stream 不能包含 delete record或者 retract record
function 必须是 row_number
processElementWithRowNumber 这个加rowNumber 对于下游处理不当来说 是会产生问题的,比如hbase sink的话, 要 rownumber +所有字段作为一个 rowkey去保存,有些用户 rownumber+partitionkey作为 rowkey字段, 内部是按整条数据 rownumber + partitionkey+ sortkey 来update和 retract删除,只靠 2个字段来删除 最终的数据 是不正确的 processElementWithoutRowNumber 不需要 rank的情况下,不用动 rank的名次,该条数据在topN中,只需要 更新该条数据即可,有 踢数据的情况的话就要加数据和踢数据
RetractSortedRank
Input stream can contain any change kind: INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE_BEFORE and UPDATE_AFTER
isAccumulate
要处理 retract和 update的数据
原来版本State里面是保存 全部数据,只在registerProcessingCleanupTimer 进行清理
增加了KeyedSortedMapState 和 TopNBuffer 要比 TopN里面存的数据要多的
Window
Async-IO
文档信息
- 本文作者:Jessica
- 本文链接:https://jessica0530.github.io/2020/08/21/Flink-SQL-Calc/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)